
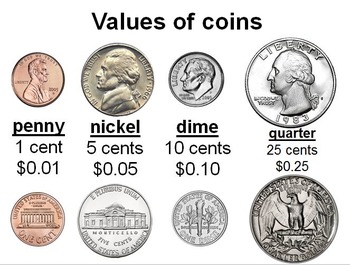
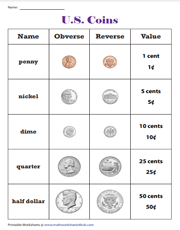
The wheat cent was mainstream and common during its time.However, cents minted from 1944 to 1946 were made from a special salvaged WWII brass composition to replace the steel cents, but still save material for the war effort, and are more common in circulation than their 1943 counterparts. These "steel pennies" are not likely to be found in circulation today, as they were later intentionally removed from circulation for recycling the metal and by collectors. Cents minted in 1943 were struck on planchets punched from zinc-coated steel which left the resulting edges uncoated. Both types were minted in 1982 with no distinguishing mark. The mass and composition of the cent changed to the current copper-plated zinc core in 1982.For table standards, see the coin specification table. These images are to scale at 2.5 pixels per millimetre. Various designs, honoring an innovation or innovator from each state See article: American Innovation dollars 9 Seal of the president of the United States surrounded by 50 starsĢ007–2016, 2020 (after 2012 not for circulation) See article: America the Beautiful quarters Most such coins that still exist are now in the hands of collectors and museums. The CC, O, C, and D mint marks were used on gold and silver coins for various periods from the mid-19th century until the early 20th century by temporary mints in Carson City, Nevada New Orleans, Louisiana Charlotte, North Carolina and Dahlonega, Georgia. S and W coins are rarely found in general circulation, although S coins bearing dates prior to the mid-1970s are in circulation. Denver coins bear a letter D, San Francisco coins bear a letter S, and West Point coins bear a letter W. Among marked coins, Philadelphia coins bear a letter P. Unmarked coins are issued by the Philadelphia mint. The identifying letter of the mint can be found on the front side of most coins, and is often placed near the year. The producing mint of each coin may be easily identified, as most coins bear a mint mark. The proof and mint sets are manufactured each year and contain examples of all of the year's circulating coins. Philadelphia and Denver produce the dies used at all of the mints. The West Point Mint produces bullion coinage (including proofs).

The San Francisco Mint produces regular and silver proof coinage, and produced circulating coinage until the 1970s. The Denver Mint also produces circulating coinage, mint sets and commemoratives. The main mint is the Philadelphia Mint, which produces circulating coinage, mint sets and some commemorative coins. Today, four mints operate in the United States producing billions of coins each year. The coins are then sold to Federal Reserve Banks which in turn are responsible for putting coins into circulation and withdrawing them as demanded by the country's economy. All of these are produced by the United States Mint. Also minted are bullion (including gold, silver and platinum) and commemorative coins. Today, circulating coins exist in denominations of 1¢ (i.e. New coins have been produced annually and they make up a valuable aspect of the United States currency system. Overview of coins issued by the United StatesĬoins of the United States dollar (aside from those of the earlier Continental currency) were first minted in 1792.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
